Article Written by David L. Watts, Ph.D., Director of Research of Trace Elements Inc
Originally Published in Trace Elements Newsletter Volume 31, No 1, March 2020
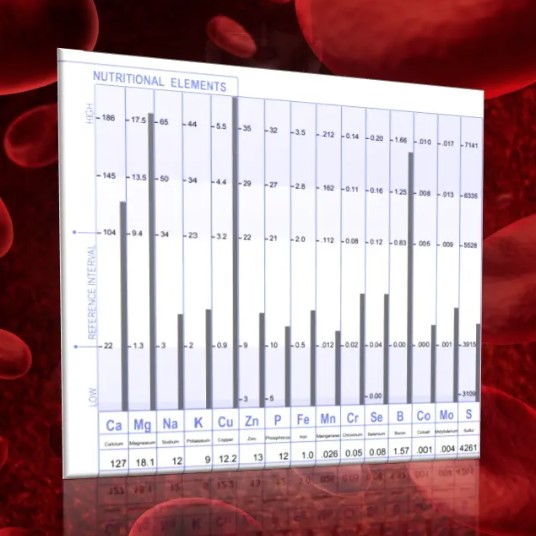
Many clients have asked questions about the metabolic subtypes that are determined in the HTMA mineral patterns. Although each type is described in individual reports, this discussion will provide further details.
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Metabolic Types
The Sympathetic Metabolic Type 1, is also known as Fast Metabolic Type 1. The Parasympathetic Metabolic Type 1 is known as the Slow Metabolic Type 1. In review, the Fast Type 1 indicates a dominance of the Sympathetic nervous system, while the Slow Metabolic Type 1 is indicative of Parasympathetic neurological dominance. Typically when the Sympathetic Nervous system is dominant the Sympathetic endocrines making up the Sympathetic Neuroendocrine System (SNES) will also be dominant and includes;
- Ventromedial Hypothalamus
- Anterior Pituitary
- Adrenal Cortex (zona fasciculata)
- Adrenal Medulla
- Thyroid
- Testosterone
Progesterone Parasympathetic neurological dominance is associated with the Parasympathetic Endocrine System (PNES) dominance and includes:
- Lateral Hypothalamus
- Posterior Pituitary
- Adrenal Cortex (anabolic)
- Thymus Pancreas (endocrine)
- Parathyroid
- Estrogen
Generally speaking the stimulatory endocrine and sedative endocrines correspond to the neurological dominance. However, due to various stages of stress the two can be intermingled.
Slow Metabolic Type 2
Below is a graphic presentation of the Slow Metabolic Type 2 mineral pattern.
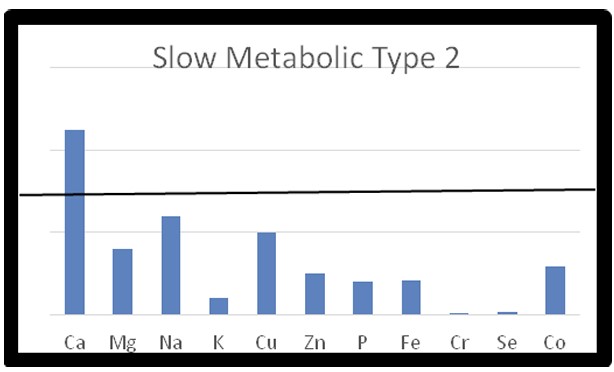
Note that sodium is elevated relative to magnesium. This pattern suggests an acute stress reaction. The stress may be physiological, psychological, or a combination of both. This would also indicate… [Continue reading the full article here]